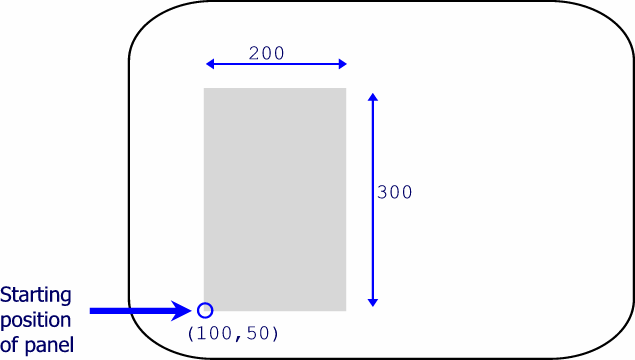
When you define a graphical region, you indicate its size by specifying its X and Y dimensions in the coordinate system of its parent. For example, the following graphical region definition tells ESL that the graphical region is a rectangular area 200 coordinate positions wide and 300 coordinate positions high. The at position specification, which defines the graphical region's origin, is the lower left corner of the graphical region.
graphical region Panel size 200 300 at position 100 50
This statement defines the graphical region Panel, which will be displayed as shown in the following example. (In the illustration, the shaded area represents the graphical region; the shading is for illustration only, and does not appear on the screen.)
Remember that when you define a region's size (as discussed in ESL's Objects and Coordinate Systems), you are actually defining two characteristics: the region's viewport and the region's window. What is displayed in the region's window is like what you would see through a camera's lens. Action Statements for Changing Windows and Viewports in Graphical Regions shows how you can change the window and viewport, effectively panning and zooming a camera.